Table of Contents
ToggleIn an increasingly digital environment, verifying users’ identities remotely has become essential to prevent fraud and ensure regulatory compliance.
What is digital proof of identity?
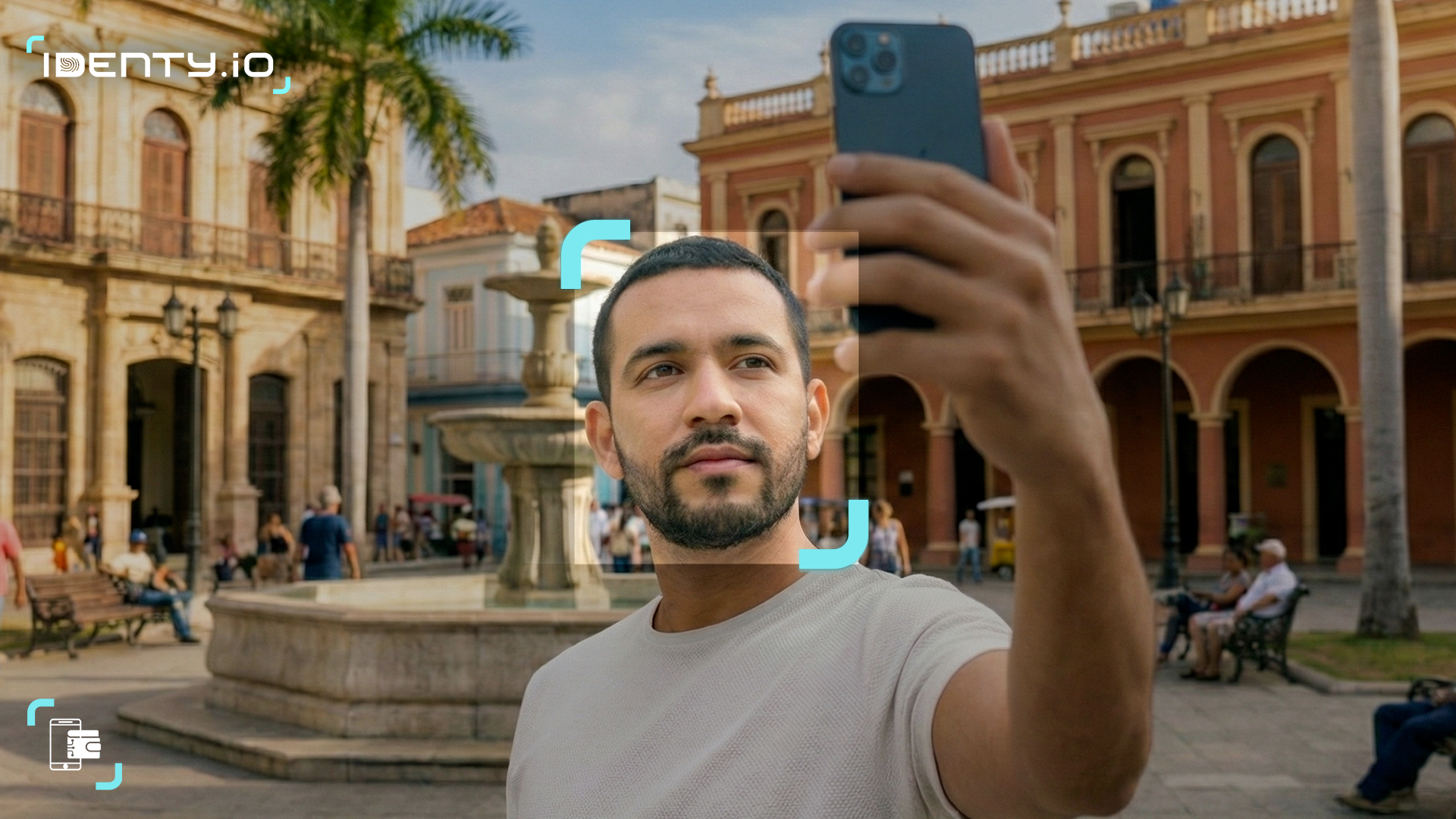
Digital proof of identity is a method used to confirm a person’s identity through digital means. In practice, the user submits digital copies of identity documents so automated systems can verify their validity and authenticity. At the same time, document data is matched to the individual through biometrics: the photo on the document is compared with a recent selfie, and a liveness test (such as blinking, smiling, or turning their head) is performed to confirm the user is physically present. Modern solutions use passive liveness detection, which runs silently in the background without requiring the user to blink, smile, or move – reducing friction and improving completion rates compared to older active methods that interrupt the onboarding flow.The goal is to reliably ensure that the individual is real and their identity legitimate, avoiding identity fraud.
Importance of digital identity verification in KYC
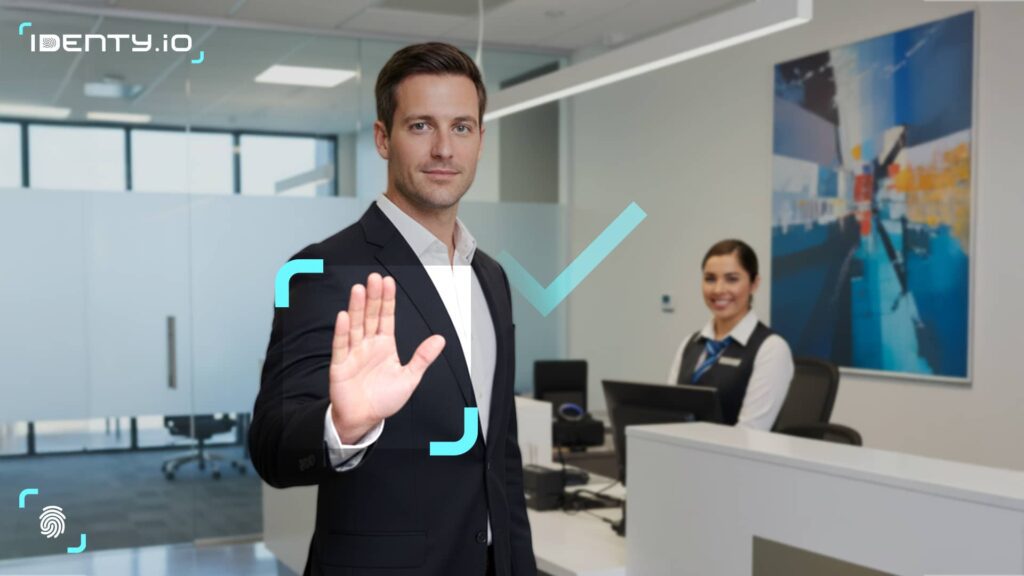
Integrating digital id verification into KYC is crucial for several reasons. It ensures regulatory compliance, as anti-money laundering laws require banks, fintech companies and other organizations to identify their customers, and digital channels enable them to do so efficiently. It also strengthens security by making identity impersonation more difficult through automated and biometric controls. Finally, it increases agility by enabling customer onboarding from anywhere in a matter of minutes, without in-person procedures, improving the customer experience and expanding business reach.
How to apply digital proof of identity in KYC
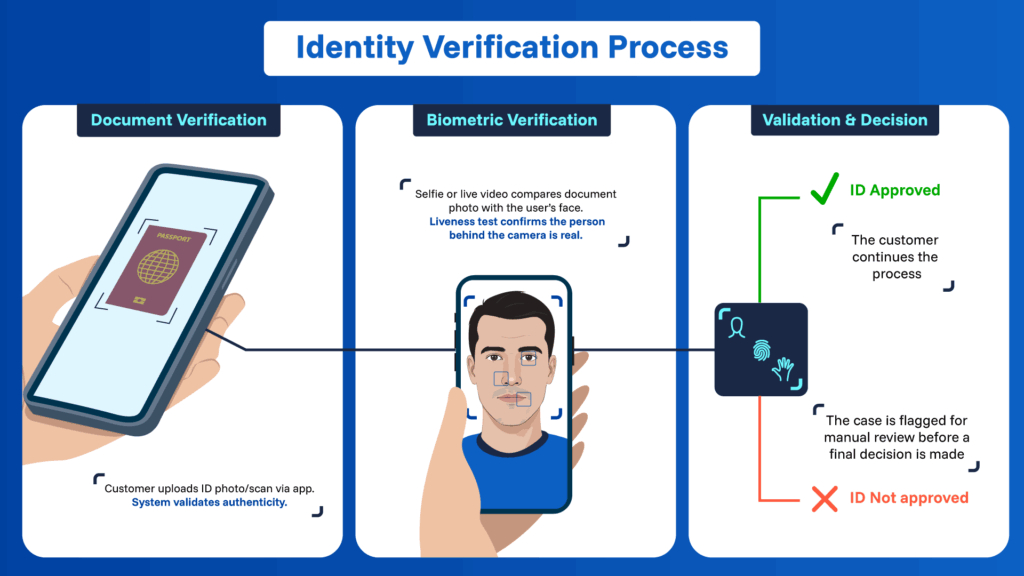
Implementing digital identity proof within a KYC workflow typically involves three key stages:
1. Document verification:
The customer provides a photo or scan of their identity document through an application or secure portal. The system checks that the document is valid (not falsified or altered).
2. Biometric verification:
The next step confirms that the person completing the process matches the document. A selfie or live video is requested, and facial recognition software compares the user’s face with the photo on the document. A liveness test (such as blinking) is also included to ensure there is a real person in front of the camera.
3. Validation and final decision:
Systems then analyze the collected information; if everything matches, the identity is approved and the customer continues the process. If discrepancies arise, the case is flagged for manual review before a final decision is made.
It is also essential to comply with data protection regulations. Collected evidence (documents, photos, etc.) must be stored securely and used only for authorized purposes. This protects user privacy and builds trust in the process.
Digital proof of identity has become indispensable for financial institutions and public administrations. Integrating it into KYC procedures enables faster and more reliable customer onboarding while complying with legal obligations. For a CMO or digital transformation leader, these solutions reduce fraud and friction in the user experience while strengthening customer trust and brand reputation. Applying digital proof of identity correctly in KYC drives innovation without compromising security or regulatory compliance.
- FAFT – Guidance on Digital ID
- European Union – eIDAS Regulation (EU 910/2014)
- European Banking Authority – Guidelines on remote customer onboarding