Table of Contents
ToggleFacial and finger biometrics are transforming how we unlock phones, open bank accounts, and verify identities online. Yet, as these systems expand, so do attempts to deceive them. The most effective defense against fake faces, photos, or deepfakes is a liveness check – the invisible step that confirms a real person is standing in front of the camera.
Deepfakes are becoming more sophisticated, increasing the risk of fraud and identity manipulation in digital environments. Download our 10-step guide to learn how to detect threats early and protect your organization with proven best practices.
What is a liveness check?
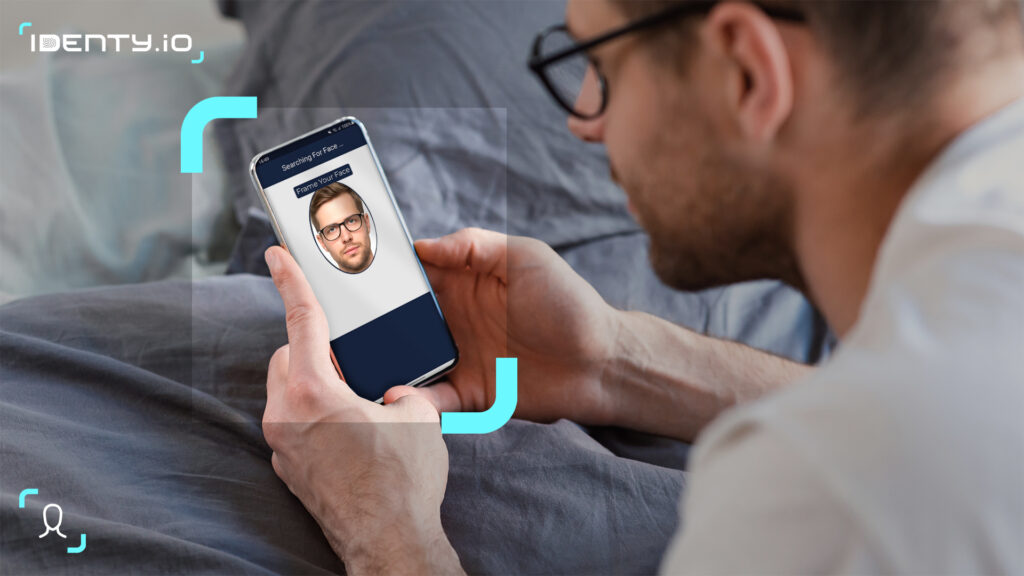
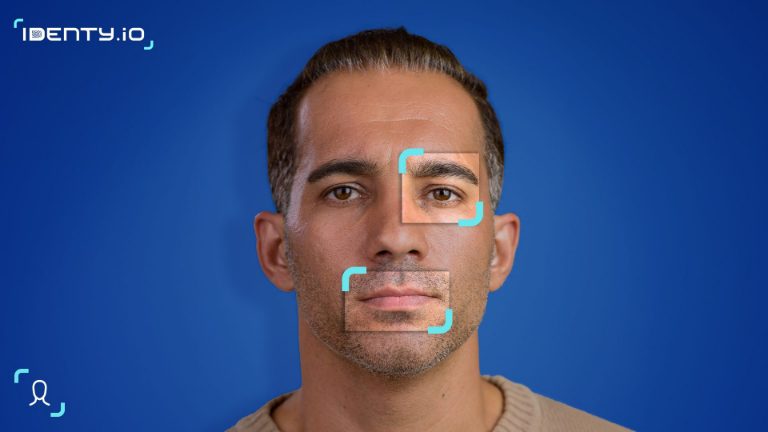
A liveness check (also called liveness detection) is a process that ensures the biometric solution interacts with a living human being, not a static image, mask, or video replay. In other words, it tells the difference between “a real face right now” and “a copy of a face.”
When you take a selfie to verify your identity in a banking app or access control system, the software analyzes subtle cues of human life — natural eye movements, skin reflections, depth, and spontaneity — to confirm that you are physically present at that moment. If the system detects signs of manipulation or artificiality, the verification is rejected.
Why liveness detection is essential
Without a liveness check, facial recognition could be easily fooled. Criminals could hold up a printed photo, replay a stolen video, or use a silicone mask to bypass authentication.
Liveness detection closes that loophole. It provides an extra layer of trust that pure image-based matching cannot deliver. By confirming that the biometric data comes from a living person in real time, the system can:
-
- Prevent identity theft and fraud in online onboarding or KYC (Know Your Customer) processes.
-
- Protect user accounts against unauthorized logins using stolen photos or videos.
-
- Ensure regulatory compliance, especially in industries that demand strong anti-spoofing standards such as ISO 30107-3 or NIST PAD. NIST results show versatility, maturity of touchless biometrics.
-
- Maintain customer confidence by guaranteeing that only real people can access secure systems.
In short, liveness detection is the difference between simple convenience and genuine security.
Get a tailored demo of our contactless biometric platform and see how it fits your specific use case.
How liveness checks work
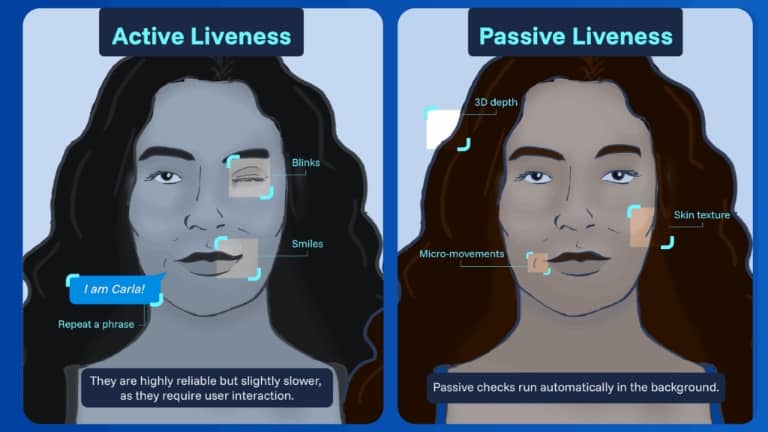
Active vs passive liveness detection
There are two main ways to verify liveness, and each balances usability and security differently.
1. Active liveness detection
This approach asks users to perform a quick action – for instance, blink, smile, turn their head, or repeat a phrase. The system checks whether the response happens naturally and in sync with the prompt. If the movement matches expectations, the user is considered alive and authentic. Active methods are highly reliable but slightly slower, as they require user interaction.
2. Passive liveness detection
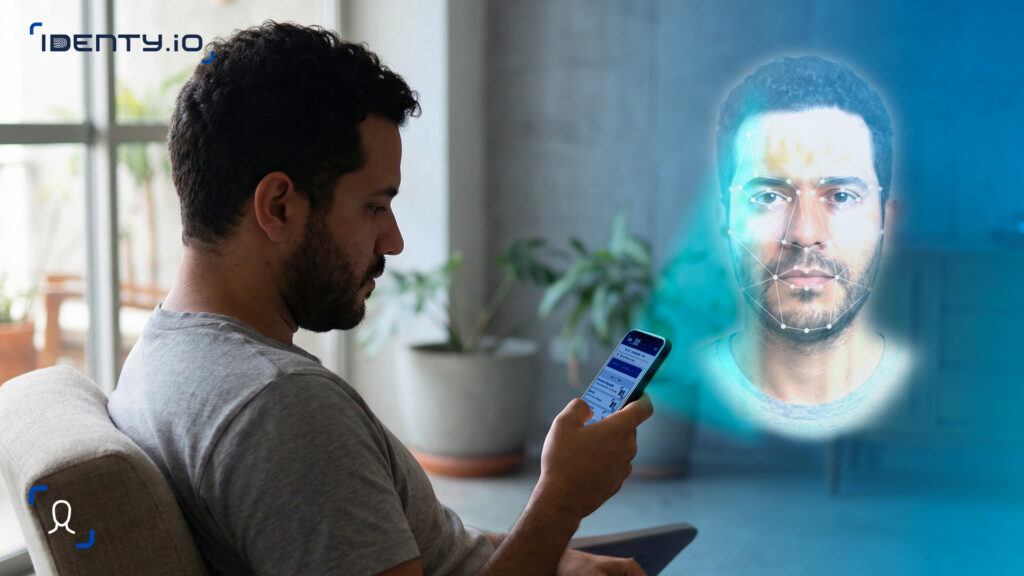
Passive checks run automatically in the background. The user simply looks at the camera, and the system analyzes the captured image or video for subtle signs of life – skin texture, 3D depth, micro-movements, or natural light reflections.
Because no extra step is needed, passive liveness delivers a frictionless experience and has become the preferred choice for modern mobile authentication.
Attacks liveness detection prevents
Liveness technology is designed to stop a wide range of spoofing attempts, including:
- Photo or video replay attacks: showing a printed or digital image to the camera.
- Mask attacks: using 3D masks, silicone replicas, or molded faces to imitate someone.
- Deepfake attacks: presenting an AI-generated video that mimics a real person’s expressions in real time.
Each of these techniques tries to trick facial recognition by presenting something that looks real but isn’t alive. Liveness algorithms examine motion, texture, temperature, and depth to reveal the difference between an imitation and a genuine human face.
Learn how Identy.io strengthened mobile security in the banking sector with advanced fingerprint biometrics and seamless user experience.
The role of liveness check in secure digital identity
As biometric authentication becomes mainstream in mobile banking, travel security, and digital onboarding, liveness detection is emerging as a critical trust layer. It guarantees that biometric data – one of the most personal forms of identification – is used responsibly and safely.
Organizations that implement strong liveness checks can:
- Reduce fraud losses from account takeovers and fake registrations.
- Meet compliance standards in financial and governmental services.
- Streamline user experience by verifying identity instantly without manual review.
For users, it means peace of mind: even if someone has their picture, they cannot impersonate them without being physically present.
Looking ahead: liveness and the future of biometrics
The next generation of facial recognition relies on AI-powered passive liveness systems that learn to detect even the most realistic forgeries and deepfakes in milliseconds.
As generative AI makes synthetic media easier to produce, robust liveness detection will be the cornerstone of digital trust.
For companies deploying biometric solutions, combining accuracy, privacy, and liveness, protection is not optional; it’s fundamental to securing every identity interaction.
References
- ISO/IEC 30107-3:2017 – Information technology — Biometric presentation attack detection — Part 3: Testing and reporting.
International Organization for Standardization (ISO). - National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Face Recognition Vendor Test (FRVT) Presentation Attack Detection. - Gartner. (2023). Market Guide for Identity Verification.
Overview of industry trends and technologies in biometric identity verification. - European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA). (2022). Biometric Systems Security and Privacy Guidelines. Technical and ethical standards for implementing secure facial recognition systems.