Table of Contents
ToggleThe healthcare sector has not been immune to the trend that has led virtually all sectors to almost total digitisation. Being able to access all patient medical records from a single computer, adapt any treatment to their specific needs in real time, carry out accurate monitoring of the patient’s condition using mobile devices (smart watches, for example), allowing for maximum personalisation of services, or requesting and managing appointments from a mobile phone are just some of the main advantages of incorporating the latest technology into the daily lives of doctors and patients.
However, as in other sectors, this digitisation of services also carries certain risks. The most significant of these is the increased risk of cyberattacks involving the theft of sensitive medical data, which occur for a variety of reasons. In fact, according to the consulting firm Kroll, in 2024 the healthcare sector surpassed the financial sector as the main target of cybercriminals, with one in four data breaches involving sensitive information from this sector. In the US alone, more than 720 incidents of healthcare data breaches were recorded last year, affecting a total of 186 million user records. In the case of Change Healthcare, the breach affected approximately 100 million people.
Why have medical data and records become one of the preferred targets for cybercriminals? There are many reasons, but the possibility of obtaining names, contact details, dates of birth, social security numbers, insurance information, and even financial data, including credit card numbers, opens the door to subsequent fraud, theft, and identity theft with multimillion-dollar consequences for patients and public and private healthcare entities.
Biometrics as the key to preventing data theft in the healthcare sector
Although some attacks are carried out on the physical media on which patients’ data and personal information are stored (servers, unprotected computers), cybercriminals most commonly exploit gaps or vulnerabilities in data transmission to carry out their attacks. This has become even more frequent with the widespread use of cloud storage.
To this we must also add the technological advances that are currently benefiting fraud. The emergence of artificial intelligence, capable of accelerating the collection of critical data in seconds and, more importantly, of impersonating users in a virtually undetectable manner to carry out all kinds of fraudulent actions, has only multiplied the risks. Thus, forecasts indicate that cybercrime in Latin America will grow by 25% during this decade, especially in the healthcare sector.
What measures are necessary to prevent these cyberattacks? Prevention remains key. The user continues to be one of the main entry points for attacks, either because they themselves—as a result of phishing, for example—share their identity credentials with criminals, or because criminals have intercepted data transmission between the user’s device and the infrastructure where this information is stored in the cloud.
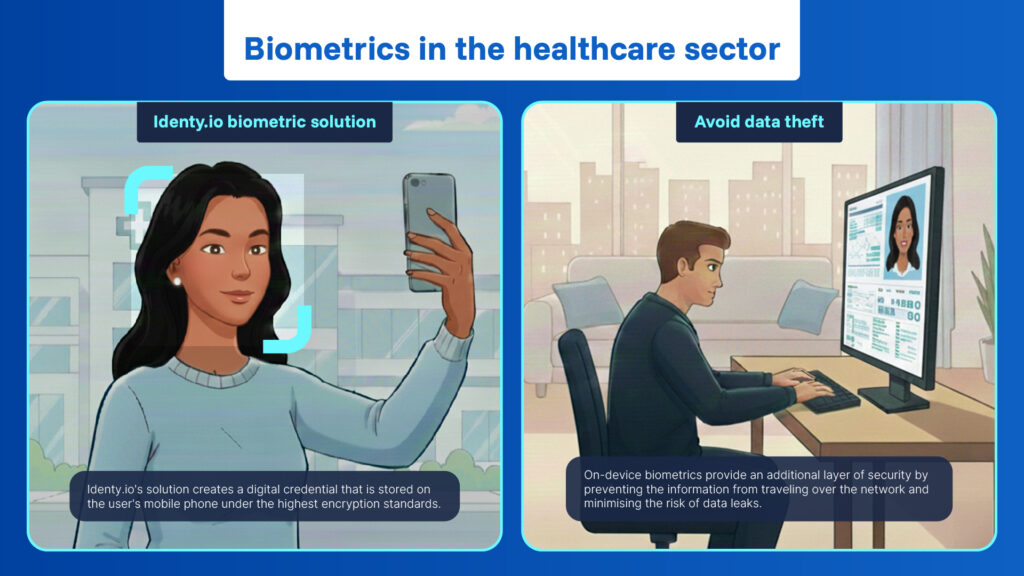
User identity verification technology is key to ensuring that the user accessing certain information is who they say they are, and not a cybercriminal impersonating them. That is why Identy.io has developed a series of solutions based on this technology that incorporate additional security measures, such as passive liveness testing, with the aim of making identity theft impossible. Thanks to passive liveness, these solutions are able to detect and reject any attempt by a third party to access the user’s personal information. This is true even in cases where the attempt is made using a digital twin created by artificial intelligence (i.e., a deepfake) or a fingerprint recreated using a high-definition silicone mould. To make the task more user-friendly, the user does not need to make any predefined movements; instead, the system determines that it is a real person by means of subtle movements in the eye, eyelid or finger.
Furthermore, unlike other solutions on the market, Identy.io’s technology uses only the user’s mobile phone to validate their identity. Once the onboarding process is complete, whereby biometric information (fingerprint, face or palm) is compared with a trusted database, Identy.io’s solution creates a digital credential that is stored on the user’s mobile phone under the highest encryption standards. Thus, whenever the user needs to access their personal data, they do so on their own device and not in the cloud or on third-party servers. This not only reduces infrastructure costs for public and private entities, but also provides an additional layer of security for the user by preventing their information from travelling over the network and minimising the risk of data theft or leaks.
To ensure maximum security and protection of the information stored on the user’s mobile phone, Identy.io solutions comply with the highest security standards, such as those proposed by the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), by supporting eKYC (Know Your Customer) ) processes and AML (anti-money laundering) frameworks, as well as complying with the ISO 30107-3 standard on liveness testing, which guarantees the security and accuracy of its portfolio of biometric identity management applications.
With the implementation of these robust and secure biometric solutions, the healthcare sector will be able to tackle the challenges posed by digital fraud, avoiding not only significant financial consequences but also significant reputational damage that can sometimes be very difficult to repair.